20 septembre 2018 | International, Aérospatial, C4ISR
The new critical capabilities for unmanned systems
By: Ryan Hazlett With unmanned systems becoming ever more ubiquitous on the battlefield, the question of where unmanned systems and accompanying technologies, such as autonomy, are headed is in the limelight. First, to better understand the future direction of the unmanned field, it is instructive to note some important trends. The number of uses for unmanned systems on the battlefield has increased significantly in the post-9/11 conflicts in Afghanistan and Iraq, with the U.S. Army's Shadow® Tactical Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) program having logged nearly 1 million flight hours in those areas of operation. The proliferation and commoditization of UAS capabilities is a global phenomenon, as demonstrated by both the widespread possession of UAS hardware as well as the ability to indigenously produce at least rudimentary unmanned systems. Growth of the nascent commercial unmanned systems market has added to this trend, as has the government's emphasis on a greater use of commercial off-the-shelf solutions. But while commoditization has occurred at the platform level — particularly among smaller airborne vehicles — overcoming the challenges of adversaries employing anti-access area-denial (A2AD) military strategies requires far more capable solutions than simply having hordes of cheap drones. In this environment, how will U.S. and allied forces retain their advantage? Critical capabilities and technologies are necessary. These include the ability to dynamically swarm, conduct automatic target recognition, possess on-board autonomy and artificial intelligence, as well as have interoperable communications capabilities. First, future platforms — manned or unmanned — will increasingly need better collaboration between the sensors and payloads they carry and with allied forces. This growing level of collaboration and autonomy is already happening. Driven by advances in onboard computing power, as well as smaller and less power-intensive sensors and advanced algorithms, tomorrow's unmanned systems will be able to better communicate among themselves and make their own decisions on basic functions, such as navigation, to enable dynamic swarming or to identify areas of interest during intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance missions. Next, systems that can seamlessly operate and communicate with other military platforms across domains will be the most successful. Gone are the days when largely mission-specific platforms dominated the force composition. With platforms needing to be highly capable to meet A2AD threats, a mission-specific approach will simply be unaffordable. Instead, increasingly we see platforms that can act as highly capable but also flexible “trucks” that can easily swap payloads designed for specific missions, while the overall platform serves many needs. Multi-domain abilities for conducting command and control (C2) and other tasks will also be vital as technologies move from remote-control type operations to more of a “man monitoring the loop” concept. Technological progress in providing secure communications and a level of onboard artificial intelligence are necessary enablers, as will be data fusion technologies. Initial versions of these multi-domain C2 solutions for unmanned systems are already here. For example, the U.S. Army has years of experience operating the Universal Ground Control Station and One System Remote Video Terminal that allow soldiers in tactical units to access overhead sensor video from unmanned aircraft. Next-generation, multi-domain control and collaboration technologies to take the concept to a new level are mature, allowing a single user to simultaneously operate multiple vehicles and sensors, including the ability to control numerous types of aircraft and other multi-domain unmanned systems from different manufacturers. In addition, these systems are ready to incorporate the best available software applications as “plug-ins” to an open architecture. Industry is also investing in additional technology to ensure that tomorrow's unmanned systems continue to meet U.S. and allied needs. Among them are advanced power generation, systems with improved maneuverability, and vehicles designed to deploy with lighter support and operational footprints. Done smartly, the application of technologies such as autonomy can be better integrated into unmanned systems to enable improved navigation, intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, as well as other tasks, while leaving a man in the loop for the use of weapons. Moreover, defense users can rightly leverage the commercial sector's work on areas such as self-driving cars and unmanned taxis that are at the forefront of artificial intelligence for navigation. But while the military can leverage such commercial developments, there are, and will remain, cyber hardening, survivability and other specific requirements that are unique to the defense marketplace and require experienced industrial partners with deep knowledge of national security needs. The ongoing move away from only long-term programs of record to the embrace of the “buy, try, and decide” model, as well as greater uses of funded prototyping, is helping to fast-track many of these promising new technologies. Companies can now match their internal research and development funding to move that innovation along and ensure the United States and its allies remain at the forefront of unmanned technologies. Ryan Hazlett is senior vice president at Textron Systems. https://www.c4isrnet.com/thought-leadership/2018/09/19/the-new-critical-capabilities-for-unmanned-systems
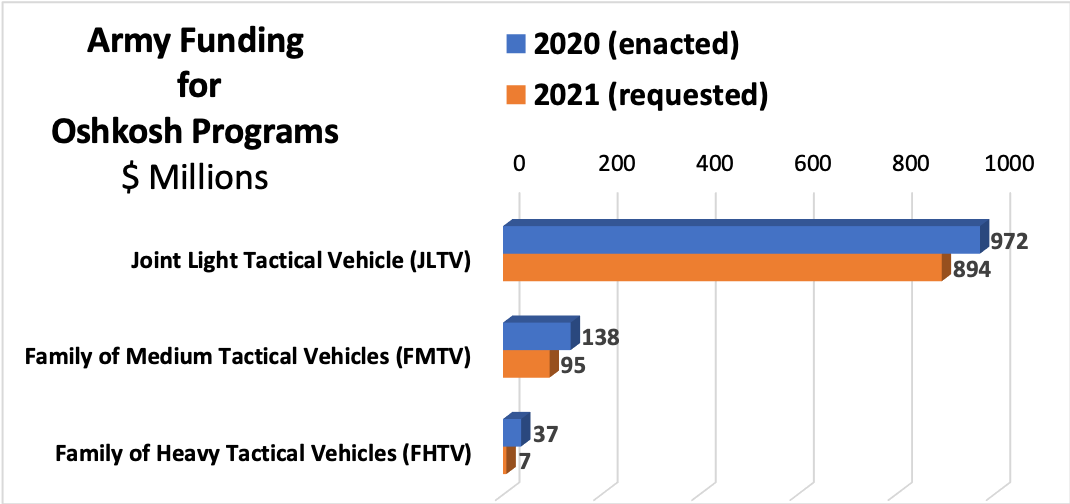 That's especially worrying for the Wisconsin company, because JLTV is
That's especially worrying for the Wisconsin company, because JLTV is 