Overall, costs of major DoD acquisition programs have grown by 54 percent over their lifetimes and schedule delays average two years, GAO's annual report finds.
By THERESA HITCHENS
WASHINGTON: Five years after the Pentagon demanded every weapon system include the requirement that it be able to fight through Russian and Chinese cyber attacks expected on future battlefields, DoD “does not often include cybersecurity” in key performance parameters (KPP) for major programs, says GAO in its annual defense acquisition review.
Of the three services, the Air Force is the worst at fulfilling two of the three best cybersecurity practices, the report says. The congressional watchdog found “inconsistent implementation of leading software practices and cybersecurity measures” among high-dollar “major defense acquisition programs” (MDAPs) — 85 programs worth $1.80 trillion at the end of 2019.
“This included longer-than-expected delivery times for software and delays completing cybersecurity assessments— outcomes disruptive to DOD's efforts to keep pace with warfighters' needs for enhanced, software-dependent capabilities and protect weapon systems from increasingly sophisticated cybersecurity threats,” GAO said in the June 3 report.
Cybersecurity KPPs Left Out
The GAO report explains that KPP “are considered the most critical requirements by the sponsor military organization, while key system attributes (KSA) and other performance attributes are considered essential for an effective military capability.” In 2015, DOD modified its main requirements policy—the Joint Capabilities Integration and Development System Manual (JCIDS) rules on “survivability” requirements to include the ability to operate in a “degraded cyber environment.”
Yet, GAO found that, at the end of 2019, 25 of the 42 major acquisition programs reviewed regarding cybersecurity practices failed to include cybersecurity as a parameter in their KPPs; “even more programs reported that their KSAs did not address cybersecurity.”
GAO has targeted cybersecurity, software development and DoD-wide information technology (IT) improvement programs in its recent annual reviews because DoD weapon systems “are more networked than ever before — a change that while providing benefits for the warfighter also “has come at a cost” because “more weapon components can now be attacked using cybersecurity capabilities,” GAO explains. “Further, networks can be used as a pathway to attack other systems.”
The watchdog has found consistently that failing to bake in cybersecurity requirements to system design and development ends up costing more money and time when program offices struggle to re-engineer systems once they hit production. This is a problem that affects most types of software development; and similarly trying to upgrade or replace software to improve cybersecurity often proves impossible.
The 2019 report thus “looked at DOD's progress with developing:
- (1) strategies that help ensure that programs are planning for and documenting cybersecurity risk management efforts (cybersecurity strategies),
- (2) evaluations that allow testers to identify systems' weaknesses that are susceptible to cybersecurity attacks and that could potentially jeopardize mission execution (cybersecurity vulnerability evaluations), and
- (3) assessments that evaluate the ability of a unit equipped with a system to support assigned missions (cybersecurity assessments).”
Most of the 38 MDAPs reviewed reported creation of cybersecurity strategies. However, of the 19 major programs that require cybersecurity vulnerability evaluations — under regulations set by the Office of the Undersecretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment Ellen Lord — 11 have not completed them or failed to do so on time. Another three said they didn't have a schedule yet for doing so; and one — an unnamed Air Force program — told GAO it actually didn't know if it had undertaken the required evaluation. Indeed, the Air Force had the worst record on the evaluations, with none of its six programs having completed the evaluation processes.
Of the 42 programs, 14 told GAO they had not finished their cybersecurity assessments. GAO also “found variation among the military departments in the rates they had completed these assessments. Specifically, among the three military departments, the Army reported the best rate for programs conducting cybersecurity assessments, while the Air Force had the lowest rate.”
IT and Software Problems Plague Programs
“Over the years, weapon acquisition program officials, through their responses to our questionnaires, have consistently acknowledged software development as a risk item in their efforts to develop and field capabilities to the warfighter, and this year is no different,” GAO reported somewhat wryly.
GAO found that more than a quarter of the 42 MDAPs reviewed reported cost growth from software changes but admitted that “details
are limited” in DoD reporting.
Part of that uncertainty might be due to the fact that GAO found a number of major programs are transitioning to commercial approaches to software development, such as “agile development” that involves introducing incremental improvements over time. However, GAO found, “deliveries often lag
behind industry standards.”
Indeed, Air Force acquisition czar Will Roper told a webinar yesterday sponsored by Dcode, a tech innovation hub connecting commercial industry to government agencies, that while the Air Force can't go back and re-do old programs, “every new contract we do has to include DevSecOps.”
“We are all in,” he added, “it's going to change the world.”
DevSecOps stands for “development, security and operations,” and is a framework and tools for “designing in” software and cybersecurity. Roper long has been a key champion within DoD for moving to commercial practices and has repeatedly said he wants the Air Force to become a “software company.”
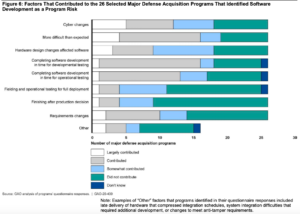
GAO said that officials from 26 of the MDAPs regarding software development reported that software concerns had created risks at some point during their program's history.
The biggest problem faced was — you guessed it — changes necessitated to ensure cybersecurity. The second biggest program was that the software development simply was “more difficult than expected.” Hardware design changes also played a big role in creating software problems, requiring subsequent changes in software configurations.
Interestingly, while often bemoaned as a cause for program delays, requirements changes came in at the low of end of the reported issues troubling software development.
Of the 15 major DoD IT programs reviewed, worth $15.1 million, 10 had delays in their original baseline schedules. But on the bright side, 11 showed decreased life cycle cost estimates.
Further, all 15 have cybersecurity strategies as required by DoD regulations, and most reported having undertaken in 2019 at least one operational cybersecurity test.
That said, “less than half reported conducting developmental cybersecurity testing,” GAO found. And according to DoD's own “Cybersecurity Testing and Evaluation Guidebook,” GAO scolds, “not conducting developmental cybersecurity testing puts programs at an increased risk of cost and schedule growth and poor program performance.
Cost and Schedule Growth Stabilizes
As it does every year, GAO also reviewed all 85 MDAPs for cost and schedule growth, and on that front the news is good: GAO found that the programs DoD Overview “have generally stabilized non-quantity related — (i.e. meaning not related to buy more stuff) — cost growth and schedule growth.”
“Between 2018 and 2019, total acquisition cost estimates for DoD's 85 current MDAPs grew by a combined $64 billion (a 4 percent increase), growth that was driven by decisions to increase planned quantities of some weapon systems,” GAO found. “For example, DoD more than doubled in the past year the total number of missiles it plans to acquire through the Air Force's Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile program.”
And some programs actually lowered their year-average costs. GAO found that 55 MDAPs (more than half) “had lower average procurement unit costs since last year. Examples of programs with lower unit costs include the Navy's Joint Precision Approach and Landing System (16 percent decrease) and the Air Force's F-22 Increment 3.2B Modernization (15 percent decrease).”
“Also between 2018 and 2019, capability delivery schedules for MDAPs increased, on average, by just over 1 month (a 1 percent increase),” GAO said.
However, the report cautioned that cost/schedule performance looks “less encouraging as measured against their original approved program baselines.”
The report found that the major acquisition programs “have accumulated over $628 billion (or 54%) in total cost growth since program start, most of which is unrelated to the increase in quantities purchased. Additionally, over the same time period, time required to deliver initial capabilities has increased by 30%, resulting in an average delay of more than two years.
https://breakingdefense.com/2020/06/major-dod-acquisition-programs-flounder-on-cybersecurity-gao


