The Army pushed hard to field-test new tech with real soldiers. Then came the coronavirus. Now the service will have to rely much more on lab testing.
By SYDNEY J. FREEDBERG JR.on May 11, 2020 at 5:11 PM
WASHINGTON: The Army is taking a calculated risk to field much-needed network upgrades known as Capability Set 21 on time next year. To do that, the service needs to start buying radios, computers, satellite terminals, and much more in bulk this year so it can start fielding them to four combat infantry brigades in early 2021.
Many Army weapons programs are staying on schedule because they're still doing digital design work and long-term R&D, much of which can be done online. But Capability Set 21 is so far along that much of its technology was already in field tests with real soldiers — testing that has been badly disrupted by precautions against the COVID-19 pandemic.
As a result, said Maj. Gen. David Bassett, Program Executive Officer for Command, Control, & Communications – Tactical (PEO-C3T), the Army may have to rely on more testing data from the lab to make up for limited testing in the field.
“As soon as we possibly can, we're going to get this back in the hands of soldiers,” Basset told the C4ISRNet online conference last week. “In the meantime, we know an awful lot from the lab-based risk reduction that we've done.”
“The risk,” he said, “is pretty manageable.”
Risk & Return
The field tests done before the pandemic, combined with extensive lab tests, should be enough to prove the technology will work, Bassett said. In fact, the Army already largely decided what technologies to buy for the upgrade package known as Capability Set 21, he said. What it still wanted soldiers to figure out in field tests, he said, was how they would use it in the field. That feedback from those “soldier touchpoints” would help both fine-tune the tech itself and figure out exactly how much to buy of each item – say, single-channel radios versus multi-channel ones — for each unit.
Going ahead without all the planned field-testing means the Army will have to make more fixes after the equipment is already fielded, a more laborious, time-consuming, and costly process than fixing it in prototype before going into mass production. It may also mean the Army initially buys more of some kit than its units actually need and less than needed of other items. But CS 21 is a rolling roll-out of new tech to four brigades a year, not a once-and-done big bang, Bassett explained. So if they buy too much X and too little Y for the first brigade or two, he said, they can adjust the amounts in the next buy and redistribute gear among the units as needed.
It's important to make clear that the Army's new technologies have already gone through much more hands-on field testing from actual soldiers than any traditional program, and have improved as a result. In the most dramatic example — not from CS 21 itself but a closely related system — blunt feedback from soldiers and quick fixes by engineers led to major improvements in prototype IVAS augmented reality goggles, a militarized Microsoft HoloLens that can now show soldiers everything from live drone feeds to a cross-hairs for targeting their rifle.
Doing such “soldier touchpoints” early and often throughout the development process is central to the 20-year-month Army Futures Command's attempt to fix the service's notoriously disfunctional acquisition system. But to stem the spread of the COVID-19 coronavirus, the Army – like businesses, schools, and churches around the world – has dramatically cut down on routine activities.
“Units are either not training, or they're training with significant control measures put in place – social distancing, protective equipment, and things like that,” said Maj. Gen. Peter Gallagher, head of the Network Cross Functional Team at Army Futures Command. That's disrupted the “access to soldiers and the feedback loop that's been so critical to our efforts.”
Nevertheless, the Army feels it has enough data to move ahead. It may also assess that the risk of moving ahead – even it requires some inefficient fixes later – is lower than the risk of leaving combat units with their existing network tech, which is less capable, less secure against hacking and less resilient against physical or electronic attack.
2021 And Beyond
Capability Set 21 focuses on the Army's light infantry brigades, which don't have many vehicles to carry heavy-duty equipment, as well as rapidly deployable communications units called Expeditionary Signal Battalions. It includes a significant increase in the number of ground terminals for satellite communications, the generals said, though not quite as many as they'd hoped to be able to afford.
It'll be followed by Capability Set 23, focused on medium and heavy mechanized units riding in 20-plus ton 8×8 Strykers and 40-plus-ton tracked vehicles. While units with lots of vehicles can carry much more gear, they also cover much larger distances in a day. That means CS 23 will include much more long-range communications through satellites in Low and Medium Earth Orbit, “which give us significantly more bandwidth at lower latency,” Gallagher said. “In some cases, it's almost having fiber optic cable through a space-based satellite link.”
Even with CS 21 still in final testing, the Army's already gotten started on CS 23. It's reviewed over 140 white paper proposals submitted by interested companies in January, held “shark tank” pitch sessions with the most promising prospects in March, and is now negotiating with vendors.
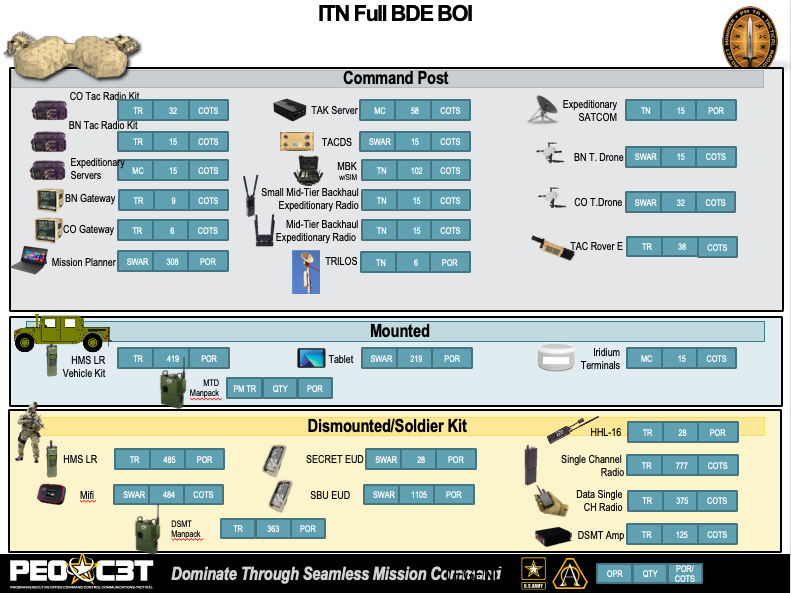
An Army slide summing up the systems being issued as part of the Integrated Tactical Network. Note the mix of Commercial Off The Shelf (COTS) and military-unique Program Of Record (POR) technologies.
There has been some impact from COVID,” Gallagher said, “[but] we will have all the contracts probably let no later than July.” The chosen technologies will go into prototype testing next year, with a Preliminary Design Review of the whole Capability Set in April and a Critical Design Review in April 2022.
Further Capability Set upgrades are planned for every two years indefinitely, each focusing on different key technologies and different parts of the Army.
Meanwhile, Bassett's PEO shop is urgently pushing out more of its existing network tech to regular, Reserve, and National Guard troops deployed nationwide to help combat COVID-19, Bassett said. That includes everything from satellite communications links to military software on an Android phone, known as the Android Tactical Assault Kit (ATAK). Originally developed to help troops navigate and coordinate on battlefields, ATAK is now being upgraded to provide public health data like rapid updates on coronavirus cases.
“Any soldier that was responding to this COVID crisis that needed network equipment, we wanted them to have a one-stop shop,” Bassett told the conference. “They would come to us and we'd go get it for them.”
https://breakingdefense.com/2020/05/covid-disrupts-network-tests-but-army-presses-on

