“I've heard some people talk about [going] back to a BCA [Budget Control Act] level of funding,” Gen. Murray says, referring to the steep cuts also known as sequestration. “And I've heard some people say that it's even going to be worse than BCA.”
By SYDNEY J. FREEDBERG JR.on May 20, 2020 at 1:11 PM
WASHINGTON: Over the last two years, the Army has cut or cancelled more than 240 programs to free billions for its 34 top priorities, from hypersonic missiles to new rifles. Some of those 34 may have to die as the economy and budget reel from the COVID-19 pandemic, .
“I start off with what Secretary Esper and Secretary McCarthy have said consistently, across DoD: three to five real growth is what we need,” said Gen. Mike Murray, chief of Army Futures Command. “Given what's going on in this country over the last two or three months.... my personal expectation is we're not going to see three to five percent growth. We'll be lucky to see a flat line.”
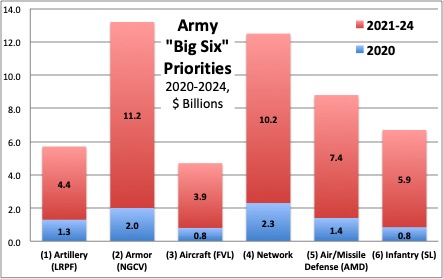
LRPF: Long-Range Precision Fires. NGCV: Next-Generation Combat Vehicle. FVL: Future Vertical Lift. AMD: Air & Missile Defense. SL: Soldier Lethality. SOURCE: US Army. (Click to expand)
While the Army is still working on its long-term spending plan for 2022-2026, the future topline is very much in doubt. “I've heard some people talk about [going] back to a BCA [Budget Control Act] level of funding,” Murray told an online AOC conference yesterday, referring to the steep cuts also known as sequestration. “And I've heard some people say that it's even going to be worse than BCA.”
“I do think budgets are going to get tighter,” Murray said. “I do think that decisions are going to get harder.”
Across its actual and projected budgets for 2020 through 2025, despite a slight drop in its topline, the Army has moved $40 billion from lower-priority programs to the 34 “signature programs.” Murray's Futures Command runs 31 of the 34, grouped in six portfolios: long-range rocket and cannon artillery is No. 1, followed by new armored vehicles, Future Vertical Lift aircraft, an upgraded battlefield network, air & missile defense, and soldier gear. Meanwhile, three most technologically demanding programs – including hypersonics and high-energy lasers – are handled by the independent Rapid Capabilities & Critical Technology Office.
“We're prioritizing what I call the 31 plus 3,” Murray said. “We have fully funded those priorities in the program at the expense of a lot of other things.”

The XM1299 Extended Range Cannon Artillery (ERCA) howitzer in an earlier test shot last year.
But Army leaders have already warned that the Big Six will need more funding as they move from concept to prototype to mass production. Even a flat budget topline will be tight — and COVID makes flat the best-scare scenario.
When and if the budget shrinks, Murray warned, “I do think we're going to have to make some tough decisions.” Hypothetically, he said, the choice may come down to something like, “Is it 31 plus three, or is it 24 plus two?”
Considering the agonies the Army went through in its multiple rounds of “night court” cuts to find money for the 34 priority programs in the first place, cancelling any of them will be painful – but not impossible.
Yes, the Army needs capabilities from each of its six modernization portfolios to work together in what's called Multi-Domain Operations against a future foe like Russia or China. Long-range precision firepower blasts holes in enemy defenses for aircraft, armor and infantry to advance; then they hunt out enemies too well-entrenched or mobile for artillery to destroy. Meanwhile air and missile defense protects the entire force, and the network passes intelligence and targeting data.
But each of the Big Six includes multiple programs, and the Army has never expected all 34 to succeed. That's a crucial difference from the service's last major modernization drive, the Future Combat Systems cancelled in 2009, which depended on each of its 20 component technologies working as planned.
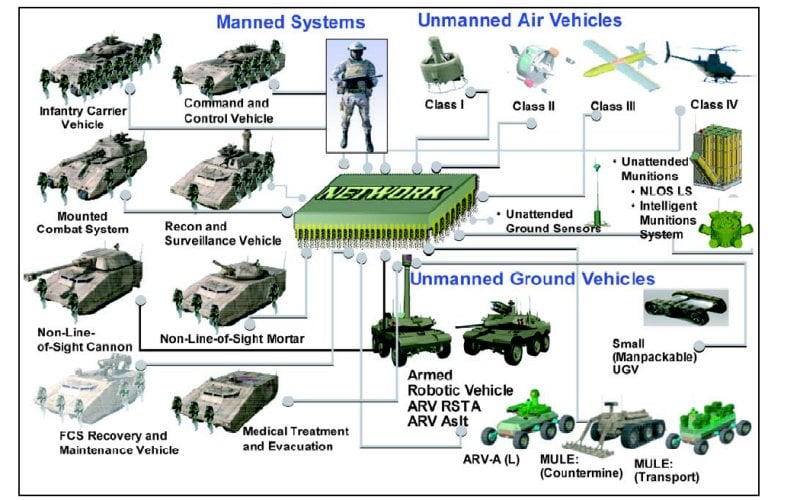
Army slide showing the elements of the (later canceled) Future Combat System
“Is there room for failures? Yes,” Murray told reporters at an Association of the US Army conference last year. “This concept does not count on any specific piece of capability.”
That doesn't make cuts painless or easy, however. “Our priorities are our priorities for a reason,” Murray said yesterday. The Army's current weapons, from missiles to tanks to helicopters, largely entered service in the Reagan era. They've been much upgraded since, but there's only so much add-on armor, souped-up horsepower, and advanced electronics a 40-year chassis can take. The Army says it needs new weapons to take it into the next 40 years.
“The kids running around on armored vehicles today are riding... fundamentally the same vehicles I rode around in as a company commander, way back when,” Murray said. “My now five-year-old granddaughter [lives] up the road at Fort Hood, Texas... I've got eight grandchildren, and out of all of them, I have absolutely no doubt that she is my infantry company commander wearing an Airborne Ranger tab at some point in the future. So that makes it personal for me.”
https://breakingdefense.com/2020/05/army-braces-for-post-covid-cuts-gen-murray



